COPYCLIP & COPYBASE Commands in AutoCAD
How to copy objects between drawings with or without a defined base point
AutoCAD offers several ways to duplicate objects, but when you need to move geometry between drawings, the Clipboard commands come into play. Two of the most useful are COPYCLIP and COPYBASE.
Both copy selected objects to the Windows Clipboard so they can be pasted into the same or another drawing, but they differ in one key way: COPYBASE lets you specify a base point for precise placement when you paste.
Summary Table
| Command | COPYCLIP | COPYBASE |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Copy selected objects to the Clipboard | Copy objects to the Clipboard with a defined base point |
| Command line | COPYCLIP |
COPYBASE |
| Keyboard shortcut | Ctrl + C | Ctrl + Shift + C |
| Ribbon location | Home → Clipboard → Copy | Home → Clipboard → Copy with Base Point |
| When to use | For quick copy-and-paste between drawings | For precise placement when pasting |
| Paired with | PASTECLIP |
PASTECLIP or PASTEBLOCK |
Overview — Clipboard Tools in AutoCAD
AutoCAD’s Clipboard commands connect your drawing workspace to the Windows Clipboard, allowing you to move selected geometry between open drawings or even between AutoCAD and other programs that support vector data.
Unlike the standard COPY command, which duplicates objects only within the current drawing, these tools temporarily store your selection in memory for reuse elsewhere.
Clipboard transfers are especially handy for:
- Copying details, blocks, or symbols into new projects.
- Assembling title sheets from multiple sources.
- Building libraries of standard components.
The most common pair is COPYCLIP (quick copy) and COPYBASE (copy with reference point). You’ll typically paste the results with PASTECLIP or PASTEBLOCK.
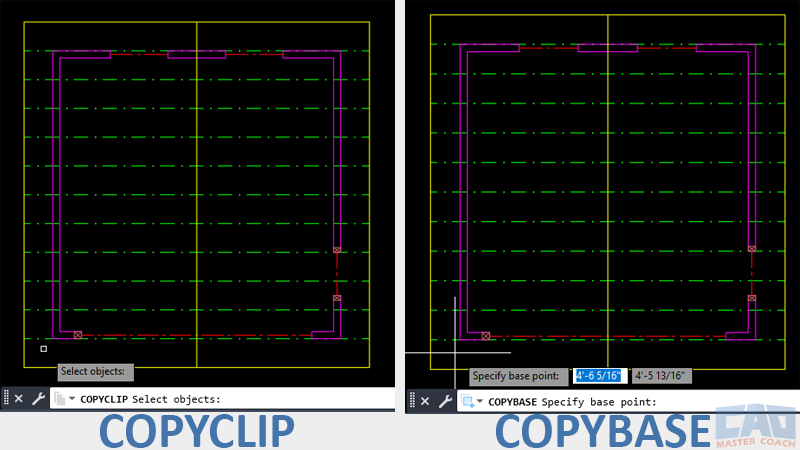
COPYCLIP copies objects quickly, while COPYBASE adds a base point for precise placement.
COPYCLIP Command Access
COMMAND LINE: COPYCLIP
DEFAULT KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: CTRL + C
RIBBON: HOME | CLIPBOARD PANEL | COPY CLIP
Purpose
The COPYCLIP command quickly copies selected objects to the Windows Clipboard so they can be pasted into the same or another drawing. It’s the digital equivalent of “Ctrl + C” in most programs, but works with AutoCAD entities instead of text or images.
How COPYCLIP Works
- Launch the command (COPYCLIP or press Ctrl + C).
- Select the objects you want to copy.
- Press Enter to finish.
- AutoCAD copies the selected geometry to the Clipboard.
- Switch to your target drawing and use PASTECLIP to insert it.
Unlike COPYBASE, COPYCLIP does not ask for a base point. AutoCAD instead stores object coordinates relative to the origin (0,0). When you paste into another drawing, the geometry appears in the same coordinate position as the original unless you specify a new insertion point.
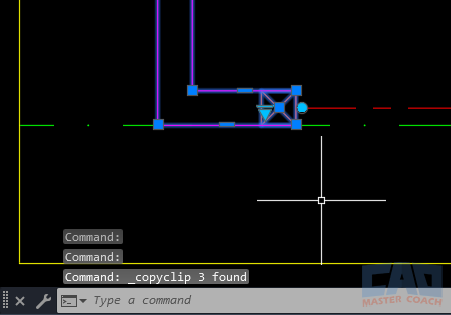
Use COPYCLIP to copy selected objects quickly to the Windows Clipboard.
When to Use COPYCLIP
Use COPYCLIP when:
- You need to move geometry between drawings quickly without worrying about precise alignment.
- You’re transferring independent elements like text, blocks, or annotations.
- You simply need to paste something into an email or another AutoCAD instance.
Because it doesn’t ask for a base point, COPYCLIP is perfect for fast, one-off transfers or when pasting into a drawing with the same origin.
Example — Copying a Title Block Between Drawings
- Open Drawing A (containing your title block).
- Type COPYCLIP and press Enter.
- Select the title block geometry.
- Press Enter to complete the selection.
- Open Drawing B and type PASTECLIP.
- Specify a new insertion point or press Enter to place at the original coordinates.
Your title block is now copied into the new drawing — no extra setup required.
COPYCLIP transfers objects to another drawing without defining a base point.
COPYBASE Command Access
COMMAND LINE: COPYBASE
DEFAULT KEYBOARD SHORTCUT: CTRL+SHIFT+C
RIBBON: HOME | CLIPBOARD TAB | COPYBASE
Purpose
The COPYBASE command performs the same general function as COPYCLIP — copying selected objects to the Windows Clipboard — but adds one crucial feature: you specify a base point before selecting the objects.
That base point acts as an insertion reference when the geometry is pasted into the target drawing. It’s the precise way to align content between drawings.
How COPYBASE Works
- Launch the command by typing COPYBASE.
- Specify the base point — this will be used later as the insertion point when pasting.
- Select the objects you want to copy.
- Press Enter to complete.
- Switch to your target drawing and use PASTECLIP or PASTEBLOCK.
- When prompted, specify where the base point should land in the new drawing.
By defining a base point, you ensure the copied objects insert exactly where you expect — perfectly aligned, with no trial-and-error placement.
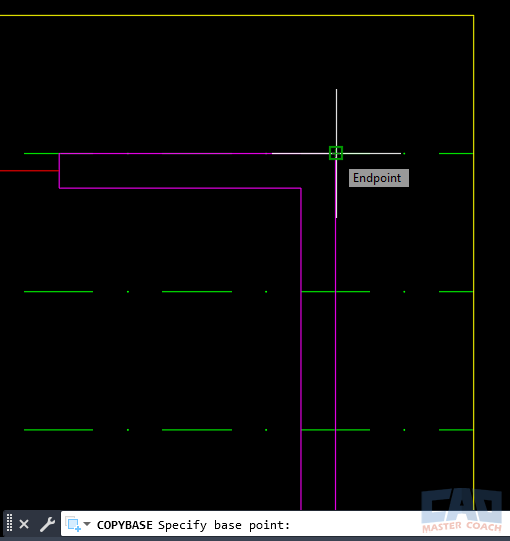
COPYBASE prompts for a base point before object selection.
When to Use COPYBASE
Use COPYBASE whenever alignment or precision matters, such as:
- Copying details that must line up with other drawings.
- Transferring geometry between floor plans, elevations, or sections.
- Inserting repeated elements that need to maintain orientation and scale.
- Creating a consistent insertion base for blocks or title sheets.
COPYBASE is especially powerful in large projects where multiple drawings share the same coordinate system — such as civil or structural plans — because it ensures everything aligns exactly between files.
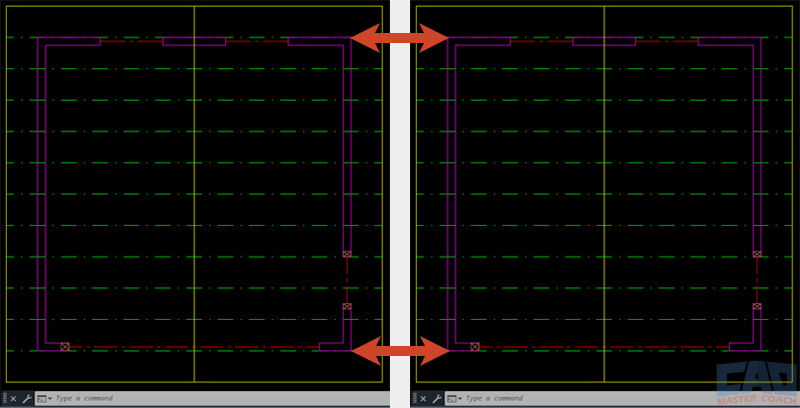
COPYBASE ensures geometry aligns perfectly across drawings.
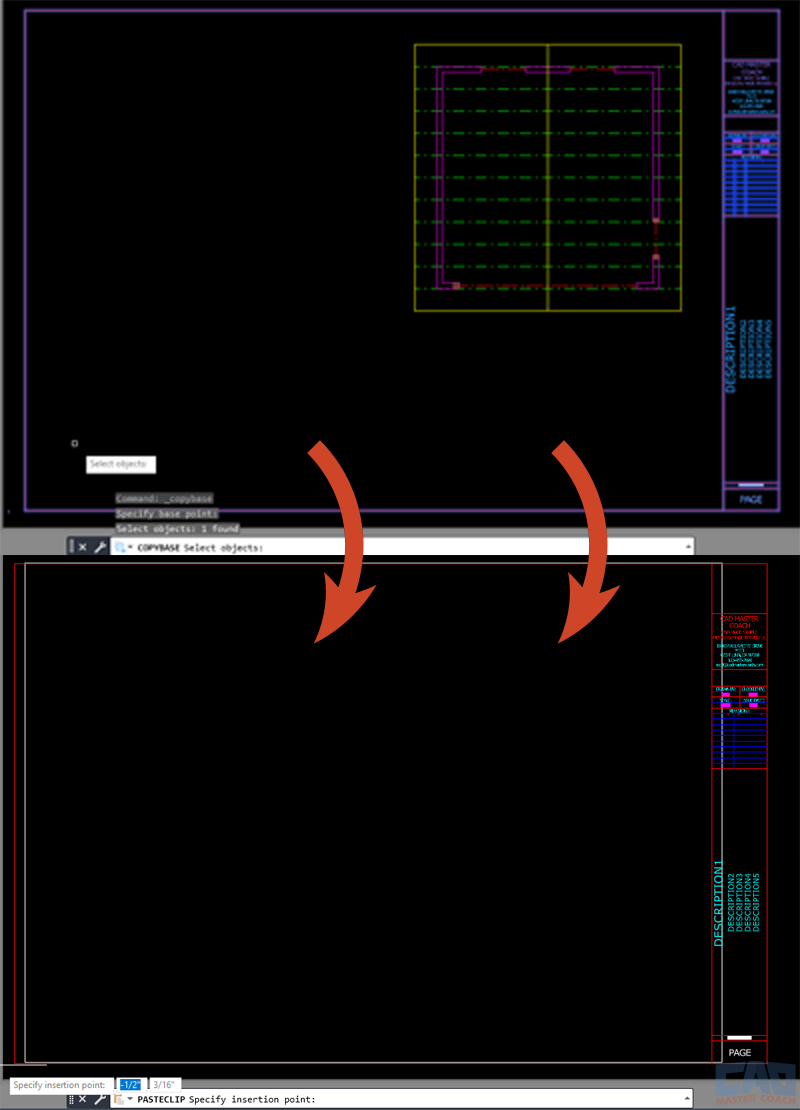
Example — Copying Geometry with a Defined Base Point
Let’s say you’ve drawn a mechanical detail in one drawing and want to reuse it in another file.
- Type COPYBASE and press Enter.
- Click the upper-left corner of the detail as your base point.
- Select all geometry in the detail.
- Press Enter to complete the command.
- Open the target drawing.
- Type PASTECLIP and press Enter.
- When prompted for the insertion point, click the same lower-left corner location — the detail drops in perfectly aligned.
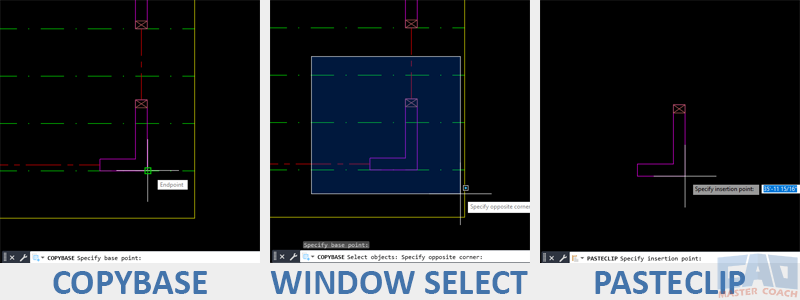
Use COPYBASE to transfer geometry that must maintain alignment.
COPYCLIP vs. COPYBASE — What’s the Difference?
Both commands copy selected objects to the Windows Clipboard, but the key distinction is whether a base point is defined.
That single difference determines whether the geometry pastes freely or with exact alignment.
| Feature | COPYCLIP | COPYBASE |
|---|---|---|
| Base Point Prompt | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Alignment Accuracy | Depends on original coordinates | Controlled by user-defined base point |
| Ease of Use | Faster – one step | Slightly slower – requires a base point |
| Best For | Quick transfers | Precise placement |
| Typical Use Case | Copying annotations, symbols, or details between similar drawings | Copying geometry that must align perfectly across projects |
| Paired Paste Command | PASTECLIP |
PASTECLIP or PASTEBLOCK |
| Default Shortcut | Ctrl + C | Ctrl + Shift + C |
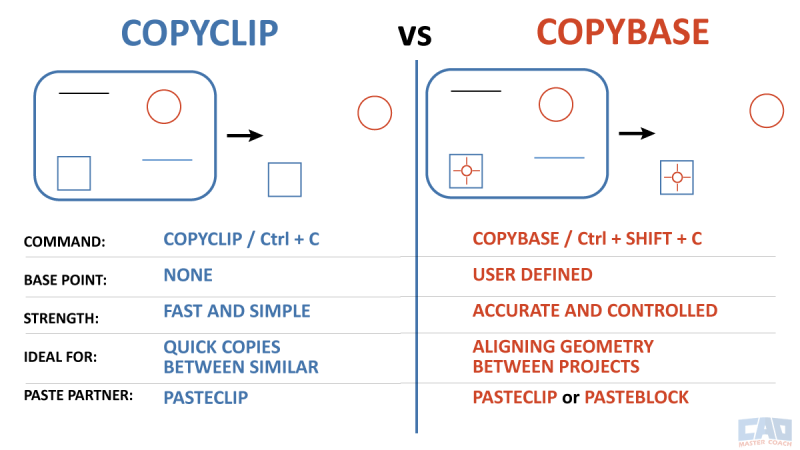
COPYCLIP is faster; COPYBASE is more precise.
Tips, Pitfalls, and Best Practices
Tips for Better Results
- Use COPYBASE when coordinate accuracy matters.
- Double-check units between files.
- Keep UCS consistency.
- Zoom Extents after pasting.
- Combine with PASTEBLOCK for reusable content.
Common Pitfalls
- Forgetting to pick a logical base point in COPYBASE.
- Assuming COPYCLIP remembers insertion points.
- Copying too much at once.
- Using COPYCLIP between drawings with different origins.
- Mixing Paper Space and Model Space.
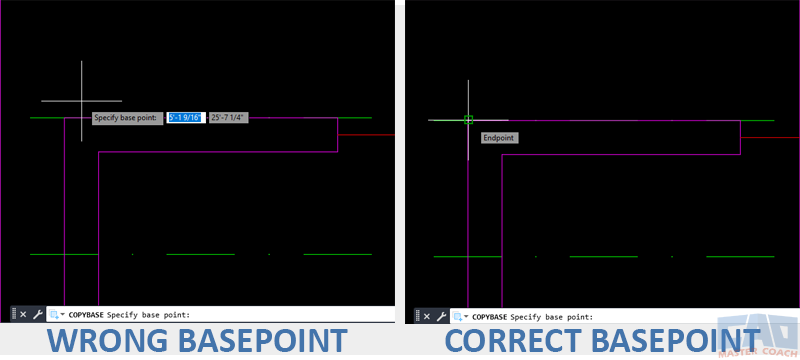
Always pick a logical base point for predictable pasting.
Related Commands
| Command | Function | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| PASTECLIP | Pastes objects from the Windows Clipboard | Use after COPYCLIP or COPYBASE |
| PASTEBLOCK | Pastes Clipboard contents as a new block | Ideal for reusable geometry |
| CUTCLIP | Cuts selected objects to the Clipboard | Moves objects between drawings |
| CUTBASE | Cuts with a defined base point | Moves geometry precisely with alignment |
| COPY | Copies objects within the same drawing | For internal duplication only |
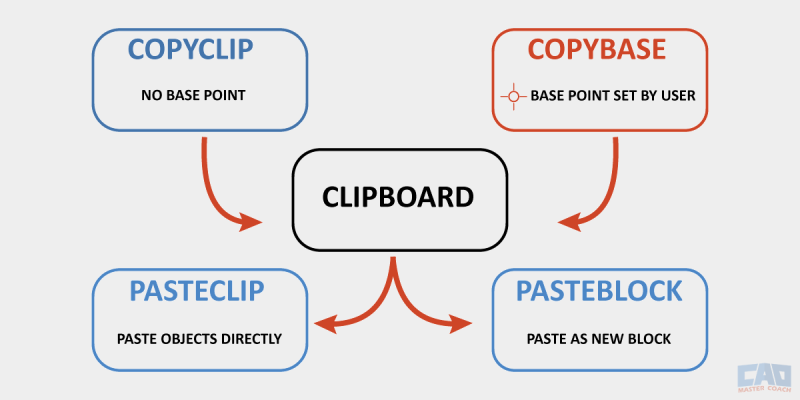
Both COPYCLIP and COPYBASE paste via PASTECLIP or PASTEBLOCK; COPYBASE includes a base point.
Summary / Quick Reference
COPYCLIP = Quick Copy. COPYBASE = Precise Copy.
| Task | Recommended Command | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Move a few annotations between open drawings | COPYCLIP | Fast, no setup required |
| Transfer details that must align with other geometry | COPYBASE | Uses a base point for precision |
| Build reusable standard parts | COPYBASE → PASTEBLOCK | Creates a block from clipboard data |
| Send geometry to another program | COPYCLIP | Works with Windows Clipboard |
| Cut and realign objects instead of copying | CUTBASE | Removes and re-inserts precisely |
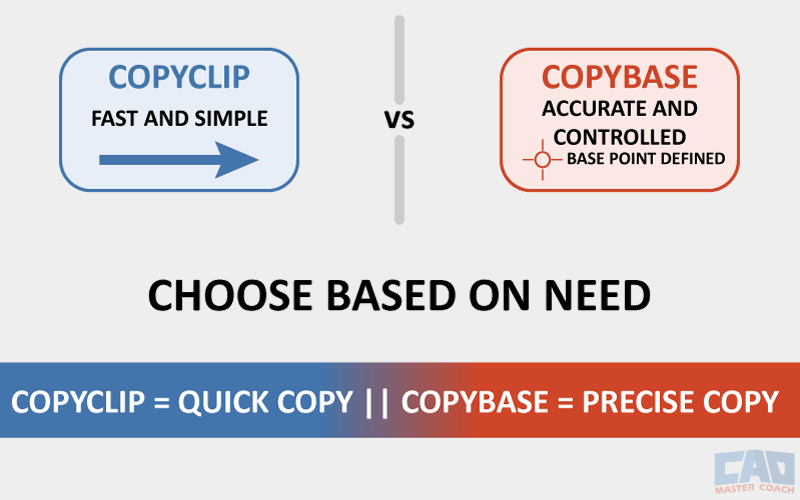
COPYCLIP for speed, COPYBASE for precision — both part of the Clipboard workflow.
Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs
COPYCLIP copies selected objects to the clipboard using their current location. COPYBASE lets you specify a base point before copying, making it easier to paste objects precisely into another drawing.
Use COPYBASE when you need accurate alignment after pasting, such as placing objects relative to a known point like a corner, centerline, or insertion reference.
No. COPYCLIP uses the objects’ existing coordinates. When you paste, AutoCAD inserts them relative to the current cursor position or the original drawing location.
Yes. Both commands place geometry on the Windows clipboard, allowing you to paste objects into the same drawing or a completely different drawing.
After using COPYBASE, use PASTE or PASTEBLOCK and snap to the same logical reference point you defined as the base point during copying.
No. COPYBASE only controls the insertion reference point. All object properties remain unchanged unless modified by paste settings or drawing standards.
Yes. Ctrl+C runs the COPYCLIP command and behaves the same way, copying objects without defining a custom base point.
Yes. COPYBASE is commonly used as a lightweight alternative to blocks when you need precise placement without managing block definitions.